Car Computer Chips

Computer Chips
|
Intel Lincoln MKZ Autonomous Self-Driving Test Car (Dec. 2016) |
The ECU Computer (Engine Control Unit)
VW's first automotive computer (1968)
The first use of a computer in a car was for engine control. Automotive manufactures began introducing early versions of computer controlled systems to perform one specific function; In 1968, Volkswagen introduced the first computer controlled electronic fuel injection (EFI) system manufactured by Bosch.Controlling the engine is the most processor-intensive job on your car, and the engine control unit is the most powerful computer on most cars. ECU's have become a standard device on most cars since the late 1970's when they became necessary due to increasingly stringent emission standards.
The ECU uses closed-loop control, a control scheme that monitors outputs of a system to control the inputs to a system, managing the emissions and fuel economy of the engine (as well as a host of other parameters).
Gathering data from dozens of different sensors, the ECU knows everything from the coolant temperature to the amount of oxygen in the exhaust.
With this data, the ECU performs millions of calculations each second, including looking up values in tables, calculating the results of long equations to decide on the best spark timing and determining how long the fuel injector is open. The ECU does all of this to ensure the lowest emissions and best mileage.
 In the early 1n as ECU (Electronic control Units). These ECU's used custom Intel 8061 (a derivative of the Intel 8096 Microcontroller) and later used 8065, 83251 & 8051 microcontroller chips for its processing functions. The 8051 and its derivatives were used in almost all Ford automobiles built from 1983 through the end of the 20'th century. In 2005, Intel announced they were discontinuing production of all automotive versions of their microcontrollers.
In the early 1n as ECU (Electronic control Units). These ECU's used custom Intel 8061 (a derivative of the Intel 8096 Microcontroller) and later used 8065, 83251 & 8051 microcontroller chips for its processing functions. The 8051 and its derivatives were used in almost all Ford automobiles built from 1983 through the end of the 20'th century. In 2005, Intel announced they were discontinuing production of all automotive versions of their microcontrollers.
Other Early Automotive Computer Controlled Systems
- 1969 - Ford introduces their first computer controlled anti-skid system.
- 1971 - General Motors introduces their first computer controlled transmission.
- 1978 - Cadillac introduces a computer controlled trip computer powered by a Motorola Microprocessor.
- 1986 - Carnegie Mellon University's "Navlab 1" becomes first self-driving, autonomous car.
- 1986 - Chrysler introduces multiplexing wire communication modules with chips supplied from Harris Semiconductor.
- 1987 - First automotive microcontroller chips produced to CAN vehicle bus standards by Intel and Philips Semiconductor.
- 2014 - First commercially available self-driving vehicle introduced - The Navia shuttle.
- 2015 - Daimler's "Freightliner Inspiration" becomes First self-driving, semi-autonomous, Semi-Truck.
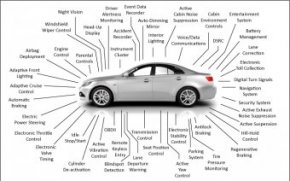
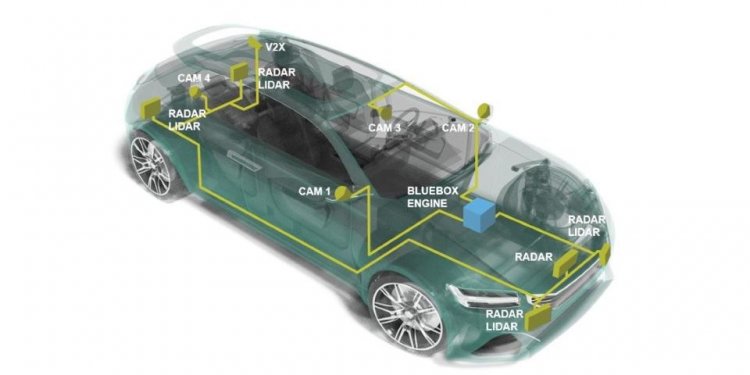
Today's Automobiles contain dozens of Computer Chips
Computers in modern cars monitor many different systems
Today, a car can have well over 50 computer systems monitoring & controlling everything from ride handling to on-board entertainment & Communication systems.
 Automakers, including Ford, GM, Tesla, VW & BMW, are working on autonomous self-driving cars which will only add to the growing number of computers found inside a car.
Automakers, including Ford, GM, Tesla, VW & BMW, are working on autonomous self-driving cars which will only add to the growing number of computers found inside a car.
Current automotive semiconductor suppliers include Freescale / NXP, Renesas, Infineon, STMicroelectronics, Bosch, Texas Instruments, ON Semiconductor, Toshiba and Micron Technology.
Some Memorabilia with Automotive Computer Technology
Intel's Computer Controlled Chopper (2007)
Intel / OCC Computerized Concept Motorcycle (2007)In 2007, Intel marked the 30th Anniversary of it's Embedded Processor Division with the creation of an Intel themed, embedded technology controlled motorcycle, built by Orange County Choppers (OCC). It was unveiled at the Embedded Systems Conference (ESC) in San Jose, Ca.
Intel's concept motorcycle featured embedded computer chips that controlled ignition by way of fingerprint recognition, a removable Black Diamond "SwitchBack" 1GHz Celeron powered ultramobile PC (UMPC) that doubled as a touchscreen to display dashboard and gauges, an infotainment system with integrated audio and video systems, rear-mounted cameras that replaced rear-view mirrors, and even an electronically controlled kickstand. The motorcycle even had Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and GPS connectivity.